It has come to light that a recent breach disclosed by Ticketmaster UK may be much larger than initially reported, with not just the company’s UK site, but also their sites for Ireland, New Zealand, Australia, Turkey and even the US found to contain digital card-skimming code. Similar to the recent breach at Harvey Norman, this incident was caused by cyber criminals compromising a third-party service provider, not the site itself directly, leading security experts to believe many more websites may be at risk or have been compromised. This is part of a concerning new trend whereby cyber criminals are targeting third-party providers, who may deal with hundreds of websites, rather than attacking a website individually, exponentially increasing the damage inflicted.
How to Check If Your Business or Personal Email May Have Been Compromised
It’s 2018, and cyber crime is on the rise. It seems every other week there is another data breach or cyber attack somewhere in the world, and many people are rightfully apprehensive that they may be hacked too, or even that their details may have been exposed online through a breach of a service that they use. What if your email and password were compromised in the Adobe breach in 2013, the Yahoo breach in 2016, or the LinkedIn breach in 2012? What if your email had been obtained online and sold to cyber criminals as part of a spam list, such as Exploit.In, or the Anti Public Combo List, both discovered in 2016? If so, you may be at risk of hackers gaining access to your accounts, or even committing identity fraud against you. Luckily, security researcher and Microsoft regional director Troy Hunt has developed a database so that you can check to see if you’ve been compromised – so you can secure your online presence again.
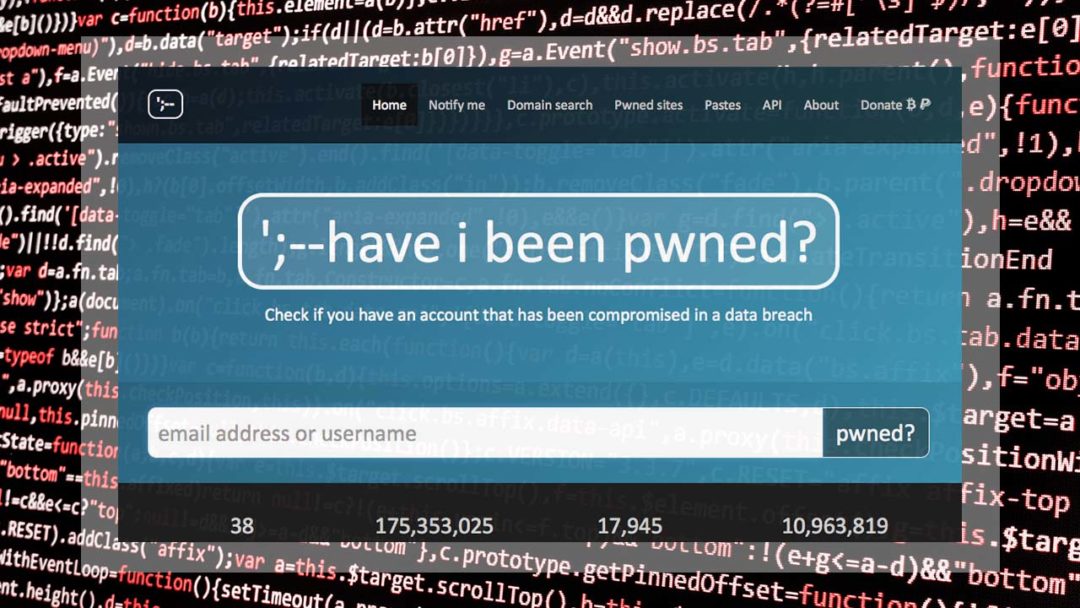
haveibeenpwned.com is a breach database run by security researcher and Microsoft regional director Troy Hunt
How the Latest Zero-Day Flash Bug Bypasses Your Antivirus and Firewall
Adobe has been forced to release an out-of-schedule emergency security patch to its users, after a zero-day vulnerability was discovered to affect Adobe Flash Player. Users are being urged by Adobe to update to version 30.0.0.113 of Flash Player, which contains mitigations for the zero-day as well as addressing three other flaws. This latest flaw was discovered already being used in the wild to attack Windows users, and doesn’t exploit browsers like typical Flash exploits – instead, it works through Microsoft Office documents which it utilises to download and execute malicious code.

Most Flash exploits take advantage of web browsers, however this zero-day utilises Office documents and is usually received through phishing emails
Less Businesses Reporting Ransomware Despite Increase In Attacks
It seems that everyone in the cyber security sphere is talking about ransomware these days. Last year, attacks such as WannaCry, NotPetya and BadRabbit took the business world by storm, costing billions in damages. Ransomware is by no means a new threat (it has been around since at least 2005), but it is one of the fastest growing and most costly. Cyber crime is constantly changing, and criminals keep creating news ways to steal money. Ransomware has gotten increasingly sophisticated since 2005, but the people using and deploying it haven’t necessarily – now some cyber criminals are making more money selling high-tech ransomware strains to non-technical criminals than if they were to conduct the attacks themselves. The result is that more and more ‘hackers’ have access to ransomware and need very little technical know-how to operate it, leading to more and more ransomware attacks each year. It may come as a surprise, then, to hear that the FBI received less reports of ransomware attacks in 2017 than in 2016 and 2015, despite the increase in attacks.

The FBI reported just 1,783 reports of ransomware attacks in 2017, compared to 2,673 in 2016 and 2,453 in 2015.
Chrome Extension Turns Unsuspecting Users Into Cryptocurrency Miners
The cryptocurrency saga continues. A malicious extension has been removed from Google’s Chrome browser after it was revealed that it had been spreading through Facebook, attempting to steal passwords from unsuspecting users and taking advantage of their PCs to mine cryptocurrency. This isn’t the first time that cyber criminals have attempted to hijack other people’s computers in order to mine cryptocurrency for them. The extension, named FacexWorm, used Facebook messenger to spread to other users, sending what appears to be a Youtube link, which actually redirected the user to a fake landing page. The extension then communicated with criminal servers in order to download further malicious code onto the user’s PC.


