It seems that everyone in the cyber security sphere is talking about ransomware these days. Last year, attacks such as WannaCry, NotPetya and BadRabbit took the business world by storm, costing billions in damages. Ransomware is by no means a new threat (it has been around since at least 2005), but it is one of the fastest growing and most costly. Cyber crime is constantly changing, and criminals keep creating news ways to steal money. Ransomware has gotten increasingly sophisticated since 2005, but the people using and deploying it haven’t necessarily – now some cyber criminals are making more money selling high-tech ransomware strains to non-technical criminals than if they were to conduct the attacks themselves. The result is that more and more ‘hackers’ have access to ransomware and need very little technical know-how to operate it, leading to more and more ransomware attacks each year. It may come as a surprise, then, to hear that the FBI received less reports of ransomware attacks in 2017 than in 2016 and 2015, despite the increase in attacks.
US & UK Blame Russia for NotPetya, Most Costly Cyber Attack to Date
The governments of the UK, US, Australia and more have publicly blamed Russia for the NotPetya ransomware attacks, which crippled businesses all over Europe back in June 2017 with a particularly nasty and destructive strain of ransomware. Last Thursday, the White House press secretary Sarah Sanders stated that NotPetya was “a reckless and indiscriminate cyber-attack that will be met with international consequences”, squarely blaming the Russuan Military and the Kremlin for causing billions of dollars’ worth of damage to businesses and states alike. The same day, the British defence secretary Gavin Williamson accused the Russian government of “undermining democracy”, after the attack, which was primarily aimed at the Ukraine, spread uncontrolled throughout Europe and beyond and caused major disruption to commerce and public services.
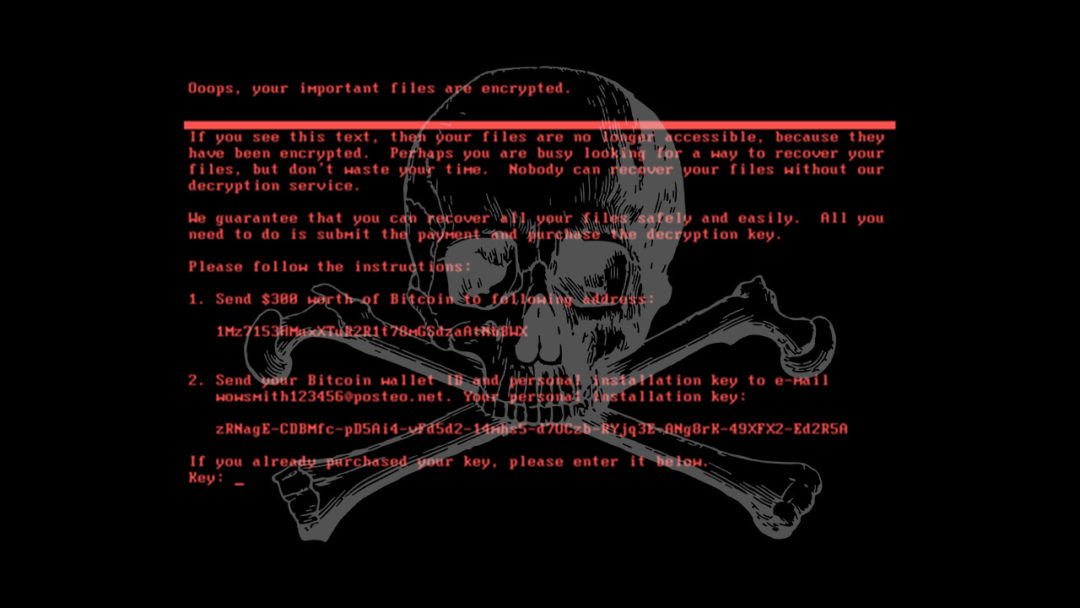
NotPetya has been described as a destructive political move disguised as a normal criminal attack seeking financial gain.
New Mass-Ransomware Strain ‘BadRabbit’ Hits Global Companies
In May of this year, the world was shook by a global ransomware attack, the now-infamous WannaCry, which is believed to have affected more than 400,000 machines. It shook the world, crippling business big and small across a wide variety of industries. It utilised a vulnerability in the outdated Windows protocol Server Message Block (SMB) v1, and Microsoft even developed a patch for Windows XP to help defend against it. How could such an attack have caught so many organisations off guard? Well, lack of patching, cited the experts, and lack of security awareness on behalf of their employees. Patch your machines now, train your staff, and you’ll be OK going forward. Then, the following month, it happened again – the world was hit by NotPetya, a ransomware strain believed to have infected a further 250,000 machines around the world. It’s worth noting that both attacks managed to affect PCs in Ireland, and that the second of the two major attacks could have been prevented if these companies had taken appropriate measures following WannaCry.

BadRabbit is the latest in a streak of mass-ransomware attacks this year, and may have been unleashed by the creators of NotPetya
As of this week, yet another strain of mass-ransomware is out in the wild, which has been dubbed BadRabbit. While it doesn’t utilise the same vulnerability as the previous two infections, its modus operandi is very similar in that it relies on both the SMB v1 protocol (which is largely defunct in 2017) and heavy use of social engineering to trick employees into clicking their malicious links. It’s an epidemic, and too few companies are learning the lessons that the cyber and business communities have gleaned from these attacks.

