Have you been hit by ransomware recently? According to a recent survey by CyberEdge, the most reliable approach (by far) to defending against ransomware is proactive rather than reactive. That is to say, having a robust backup and disaster recovery system in place is far more likely to result in minimal disruption and data loss than trying to pay the criminals in the hopes that they do the ‘honourable’ thing and decrypt your critical data. For the report, CyberEdge surveyed IT security professionals and found that more than half (55%) had been hit by ransomware in 2017. The study found that of those who had prepared for ransomware using backups and other business continuity procedures, 86.9% were able to successfully recover their data. However, of those who didn’t have backups to rely on and instead paid the ransom, only 49% actually had their data decrypted and recovered.
World’s Largest DDoS Attack Record Broken Twice in a Week
In a worrying new cyber threat trend, the record for largest DDoS (Distributed Denial of Services) attack has been broken, not once, but twice, over the past week. A DDoS attack, in essence, is an attempt to make an online service (such as your business’s website) unavailable by overwhelming it with traffic from various sources. Last week, the coding repository GitHub was briefly taken offline in a 1.3 Terrabits-per-second DDoS attack. This wasn’t entirely unsurprising, as DDoS attacks have been steadily building throughout 2018, but March has definitely been the worst month so far. Now, an unnamed US service provider has reported experiencing an even larger DDoS attack, which hit 1.7 Terrabits-per-second, only a few days after the previous record had been broken. This could pose a significant threat for many businesses that operate memcached database servers, which typically have high-bandwidth access and can be badly impacted by DDoS attacks.

At 1.7 Terrabits-per-second, the unnamed US service provider experienced the largest DDoS attack to date. These attacks are expected to increase in size and frequency going forward.
As GDPR Looms – Cyber Criminals Move Towards Business Extortion
Trend Micro, one of the largest cyber security firms in the world, has released their annual security roundup report, and the results show some alarming trends. With the GDPR upcoming, cyber criminals have been refining their techniques in order to increase their financial gains, moving away from exploit kits which can be an unpredictable earner, to more reliable tactics such as business email compromise, phishing and spam, ransomware, and the relatively new threat to businesses, malicious crypto-currency mining.

Exploits kits are down, but 2017 saw over 300 new ransomware families, in addition to a rise in business email compromise scams and the all-new malicious crypto-mining threat.
US & UK Blame Russia for NotPetya, Most Costly Cyber Attack to Date
The governments of the UK, US, Australia and more have publicly blamed Russia for the NotPetya ransomware attacks, which crippled businesses all over Europe back in June 2017 with a particularly nasty and destructive strain of ransomware. Last Thursday, the White House press secretary Sarah Sanders stated that NotPetya was “a reckless and indiscriminate cyber-attack that will be met with international consequences”, squarely blaming the Russuan Military and the Kremlin for causing billions of dollars’ worth of damage to businesses and states alike. The same day, the British defence secretary Gavin Williamson accused the Russian government of “undermining democracy”, after the attack, which was primarily aimed at the Ukraine, spread uncontrolled throughout Europe and beyond and caused major disruption to commerce and public services.
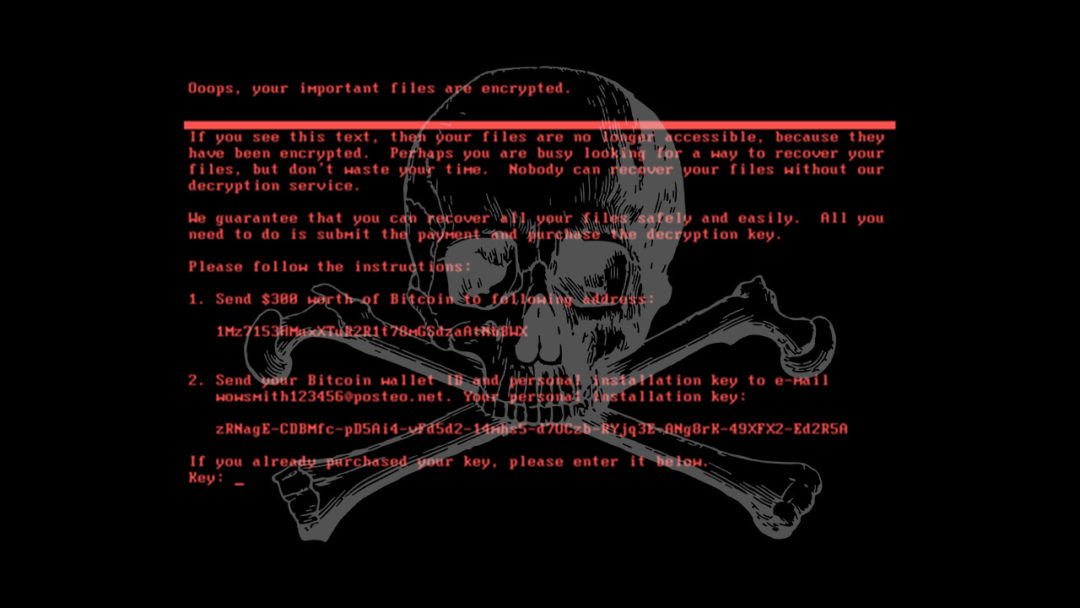
NotPetya has been described as a destructive political move disguised as a normal criminal attack seeking financial gain.
HSE, Dublin County Council, Department of Argiculture and More Hit by Crypto-Mining Cyber Attack
Ireland is claimed to be wide open to attacks from cyber criminals and rogue states, following an incident in which over 4000 websites around the world were hacked and used to mine crypto-currency. First reported by The Register, the breach affected the Department of Argicultures, Dublin City Council and Fingal, Cork, Wexford and Offaly county councils, and it is suspected to have also affected the websites of the Oireachtas, the Broadcasting Authority of Ireland, Women’s Aid and the Central Remedial Clinic. The crypto-mining attack was not limited to Irish websites, however, as the Information Commisioner’s Office in the UK, the United States courts and many more sites belonging to governments and organisations were also hit.


